Gift
Written by Raouf Ould Ali.
Problem Statement
We are given an array of size and an integer .
We start with and want to transform it into using operations of the form:
- Choose any integer
- Choose exactly distinct positions
- Add to all
The task is to either produce a valid sequence of operations with , or decide that it is impossible.
Step 1: Feasibility Conditions
Each operation increases the total sum of $B$ by $X \cdot K$.
Thus,
must be divisible by $K$.
Let
be the required “height” of each group.
If $\max(A[i]) > \text{lim}$, then one element cannot fit into a single group, so the answer is impossible.
So feasibility requires:
Step 2: Grid Interpretation
Visualize a grid of size :
- The grid has height and width .
- Each column corresponds to one bundle of size .
- We place each vertically:
- If it fits in the current column, it stays there.
- If it overflows, it continues at the top of the next column.
Since for all , a box never skips a column. At most it is split into two consecutive columns.
Step 3: Sweeping for Operations
Instead of outputting one operation per row (which could be up to rows), we notice that:
- Each column contains one index at a time.
- The index for a column only changes when one ends and another begins.
Thus, while sweeping from bottom to top:
- We keep track of the current set of active indices for all columns.
- We only output an operation when this set changes.
- The operation covers all rows since the last change, so its increment is the height difference .
Step 4: Bound on Operations
- Each can start once in a column and possibly wrap once into the next column.
- Therefore, each contributes at most two changes.
- This means the total number of operations is at most , not .
This compression is what makes the solution efficient and ensures .
Step 5: Correctness Argument
- Sum condition ensures the total number of increments matches.
- Max condition ensures no element overflows beyond a single column boundary.
- Because , there is no overlap in rows:
- Every cell of the grid is covered by exactly one index.
- The sweep construction outputs exactly the increments needed to reach , with no waste.
Therefore, the algorithm always finds a valid solution if and only if it exists.
Example
Input:
4 2
2 3 3 2- , .
- Fill the grid column by column:
Column 1: [1, 1, 2, 2, 2]
Column 2: [3, 3, 3, 4, 4]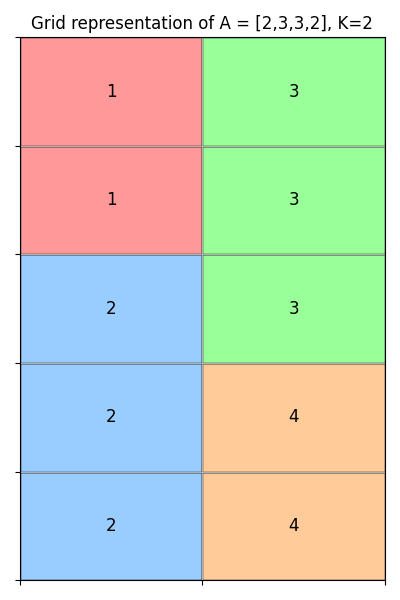
Sweep rows:
- Rows 1–2: active {1,3} → operation (2, 1 3)
- Row 3: active {2,3} → operation (1, 2 3)
- Rows 4–5: active {2,4} → operation (2, 2 4)
Output:
3
2 1 3
1 2 3
2 2 4Implementation
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
ll n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
vector<ll> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
ll sum = 0;
ll max_ai = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum += a[i];
max_ai = max(max_ai, a[i]);
}
if(sum%k != 0 or max_ai > sum/k){
cout << "-1\n";
return 0;
}
ll max_height = sum/k;
ll current_height = 0LL;
ll current_column = 0LL;
vector<vector<ll>> result;
vector<tuple<ll, ll, ll>> cache; // height, column, index
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cache.push_back({current_height, current_column, i+1});
current_height += a[i];
if(current_height >= max_height){
current_height -= max_height;
current_column += 1;
if(current_column < k)
cache.push_back({0, current_column, i+1});
}
}
cache.push_back({max_height, 0, 0});
sort(cache.begin(), cache.end());
current_height = 0LL;
vector<ll> current_move(k+1, 0);
for(auto &[height, column, index] : cache){
if(height != current_height){
current_move[0] = height - current_height;
result.push_back(vector<ll>(current_move.begin(), current_move.end()));
current_height = height;
}
current_move[column+1] = index;
}
cout << result.size() << '\n';
for(auto &x : result)
{
for(auto y : x) cout << y << ' ';
cout << '\n';
}
}
